As part of our upcoming workshop, we've created multiple no-code agents that anyone can create, use and deploy for their purposes. Let's walk through how to setup a Meeting Summarizer project that uses AIGNE to build agents who can review your meeting transcription and provide a summary with designated action item assignments. For this specific project, we are going to setup 3 agents that work together to intake the transcript, clean it up, create summaries and action items, and then display it.
Let's get started.
- Go to www.aigne.io and sign-up/sign-in to get started.
- Start a new project:
- Name: "Meeting Summarizer"
- Description: "Summarizes meeting transcripts and extracts action items."
- Select "+Create" when ready
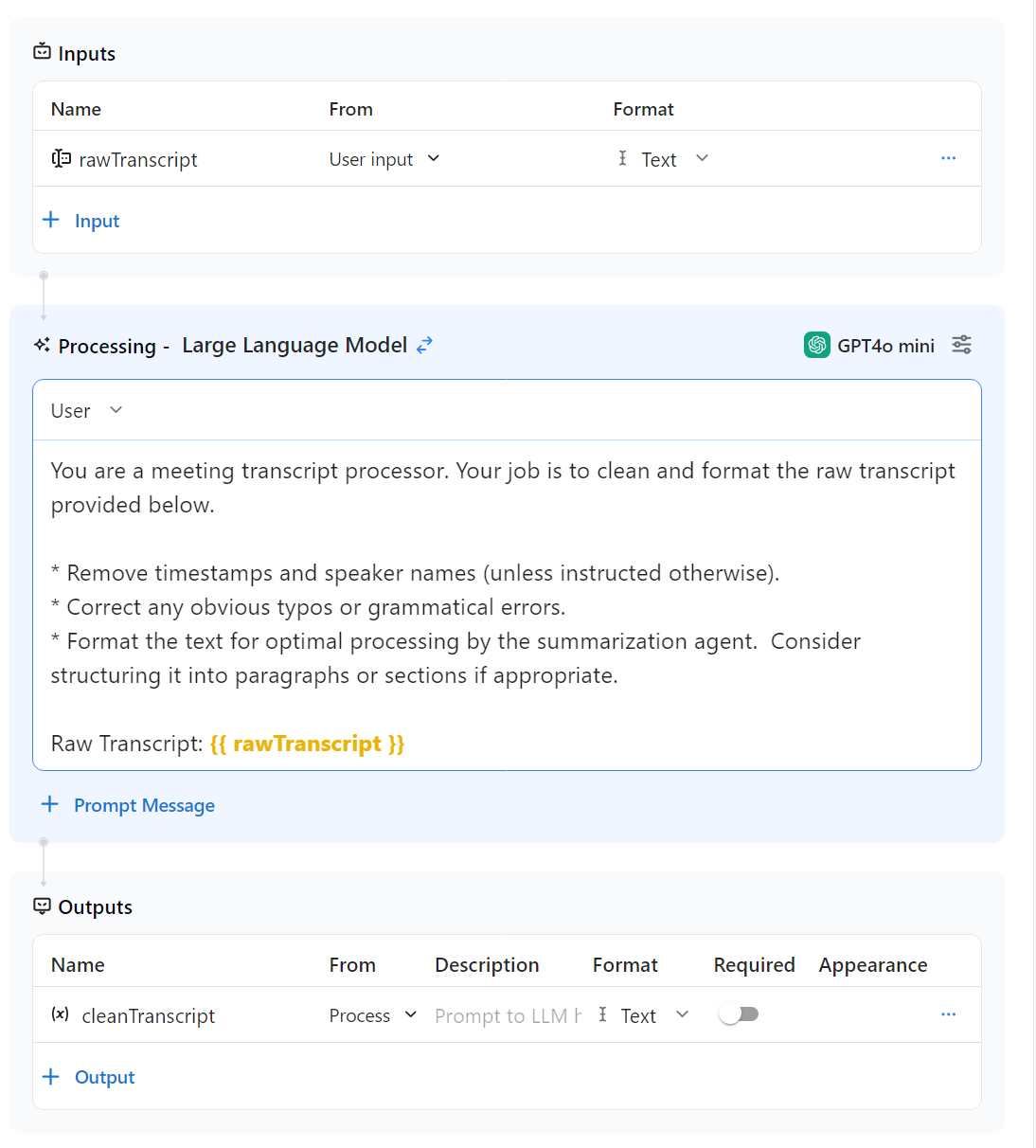
- Create Agent 1: "Transcript Processor"
- Purpose: Cleans and formats the raw meeting transcript. This might involve removing timestamps, speaker names (if desired), or correcting minor typos.
- Sample Prompt:
You are a meeting transcript processor. Your job is to clean and format the raw transcript provided below.
* Remove timestamps and speaker names (unless instructed otherwise).
* Correct any obvious typos or grammatical errors.
* Format the text for optimal processing by the summarization agent. Consider structuring it into paragraphs or sections if appropriate.
Raw Transcript:
{{ rawTranscript }}
- Set your Input:
rawTranscript(User Input) (text) - Set your Outputs:
cleanedTranscript(Process) (Text)
Example:#
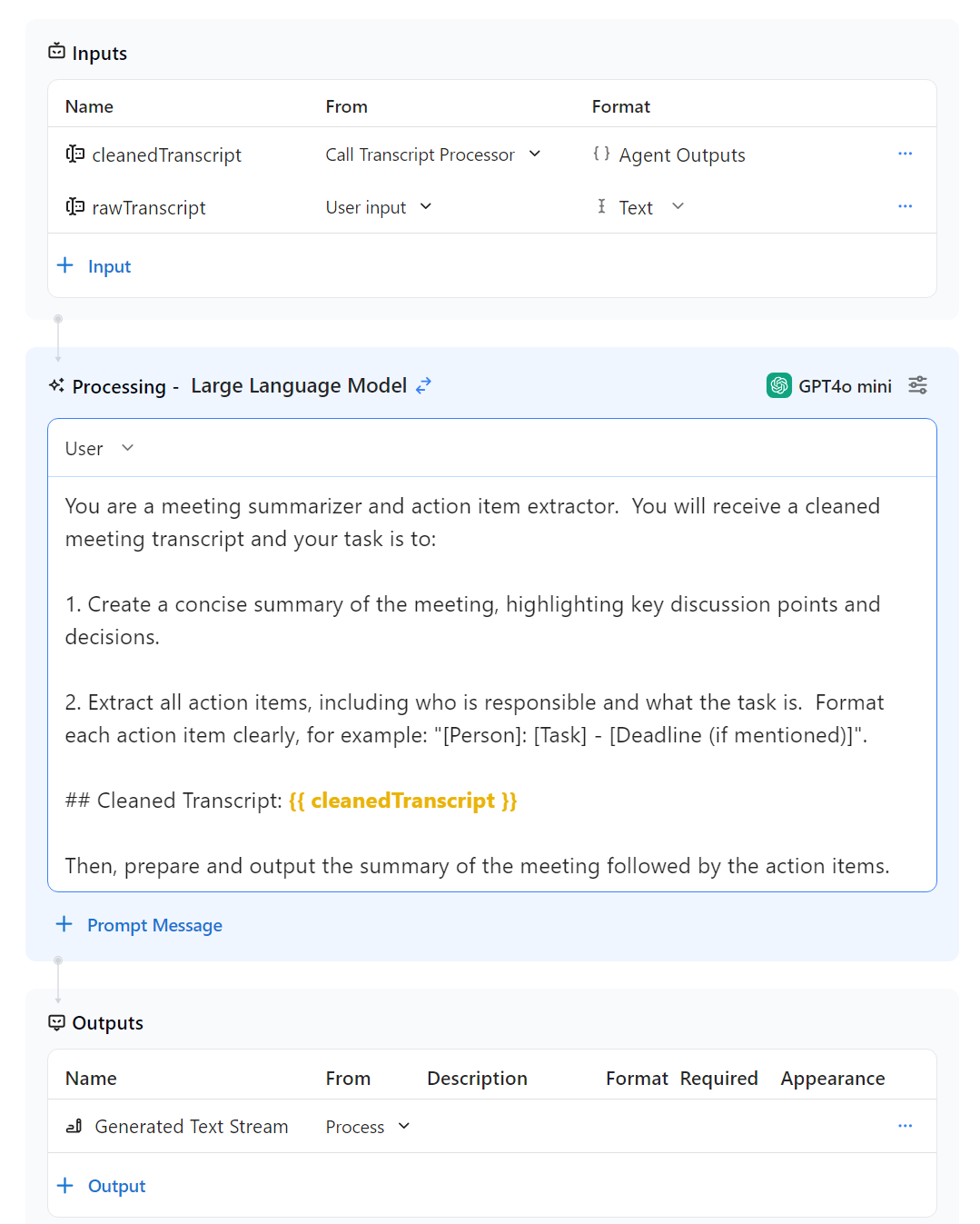
4. Create Agent 2: "Summarizer and Action Item Extractor"
- Purpose: Summarizes the cleaned transcript from agent 1 and extracts action items.
- Prompt:
You are a meeting summarizer and action item extractor. You will receive a cleaned meeting transcript and your task is to:
1. Create a concise summary of the meeting, highlighting key discussion points and decisions.
2. Extract all action items, including who is responsible and what the task is. Format each action item clearly, for example: "[Person]: [Task] - [Deadline (if mentioned)]".
Cleaned Transcript:
{{ cleanedTranscript }}
Output the summary followed by the action items.
- Inputs:
cleanedTranscript | Call Transcript Processor | Agent OutputsrawTranscript | User Input | Text
- Outputs:
Generated Text STream | Process
Example: #
5. Entry Agent: "Meeting Interface" (or similar name)
- Purpose: Provides the user interface. This agent receives the raw transcript from the user and displays the summary and action items generated by the other agents.
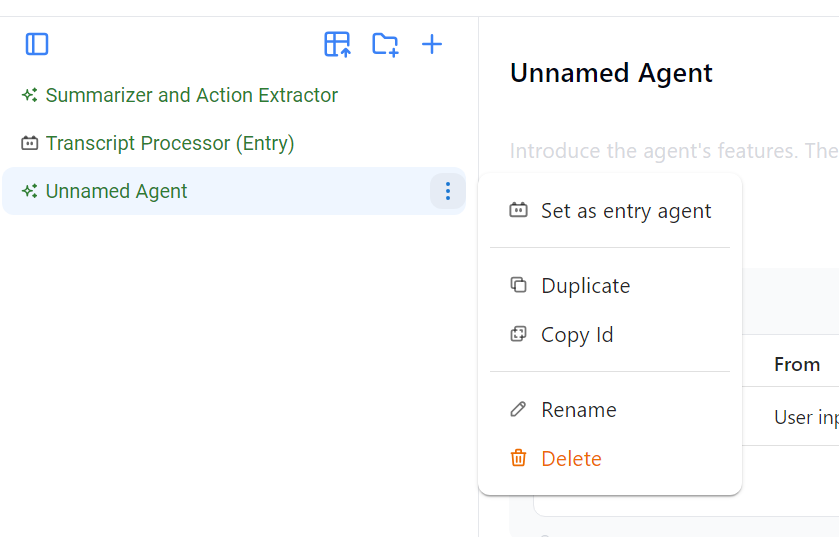
- "Set as entry Agent": Before setting up your agent, we want to first configure this agent to be the entry agent, or the UI where the user will input the information. Follow the example below and choose "Set as entry agent."
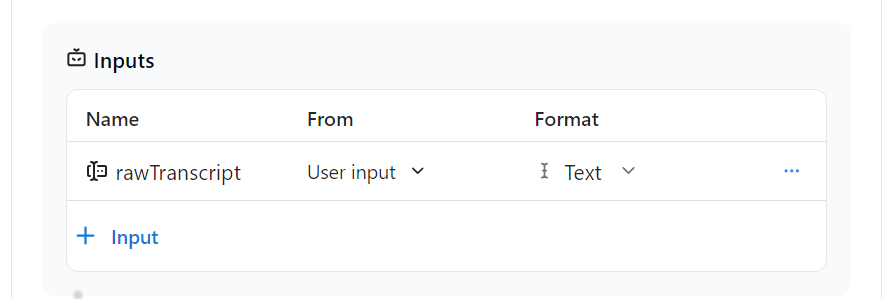
- Inputs: Set your inputs to the below options. This will be important to enable our prompt to call an agent for processing.
rawTranscript | User Input | Text
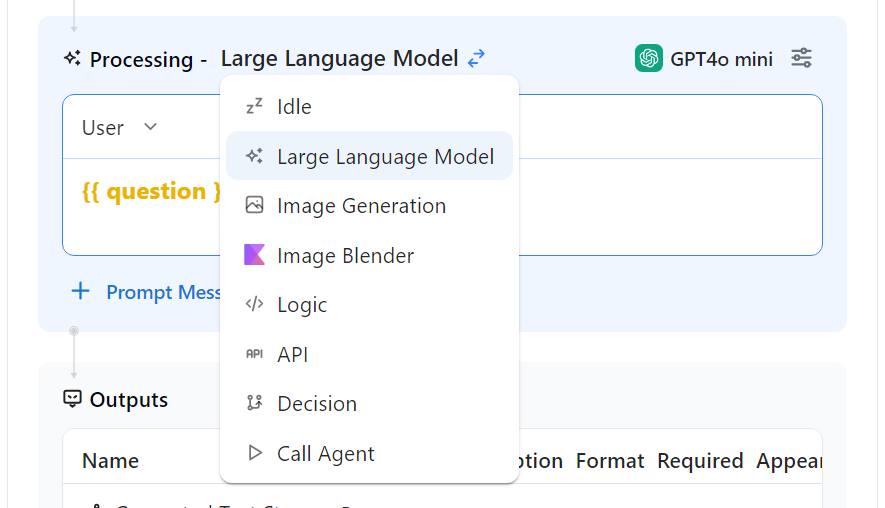
- Prompt: With your input set, now let's update the prompt.
- Step 1, select "processing" and choose "Call Agent"
- Step 2, select install more models and pick your agent. In this call, we want to call the Summarizer and Action Extractor Agent.
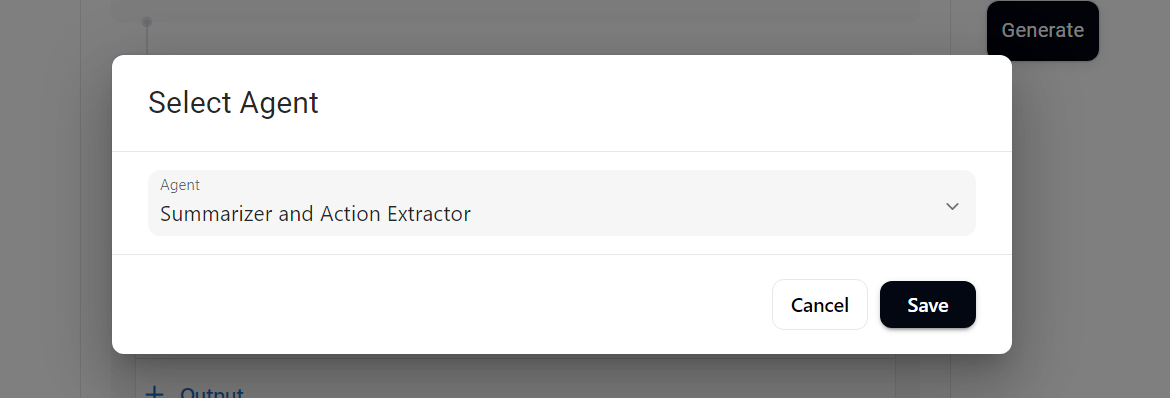
- Verify that your agent is calling the Summarizer and Action Extractor and the parameter is set for "rawTranscript."
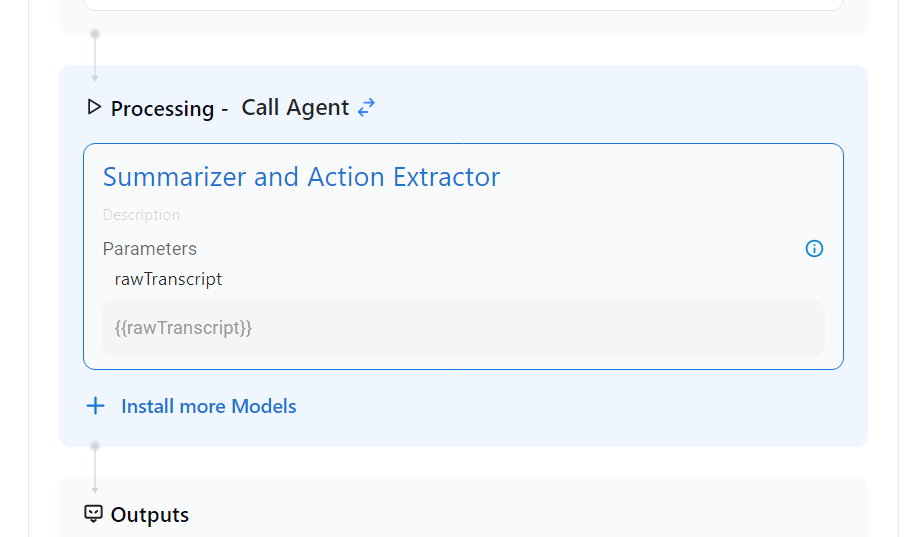
- Outputs:
Generated Text Stream
6. Test your agent configuration: Be sure your "Meeting interface" agent is selected. On the right-hand panel, select "Debug" and copy/paste a transcript into your prompt box. When selecting debug, we can get a view into what is happening behind the scenes including access to the JSON file to review the agent details.
For this example, I used a recent 48-minute meeting with the Decentralized Identity Foundation that had over 20 speakers on the call. After entering your transcript, your agent will review the transcript and output a meeting summary and specific action items, as shown in the example below.

7. With your testing done, let's Deploy the project to make it accessible to users. Select "Deploy" and choose the option that you prefer.
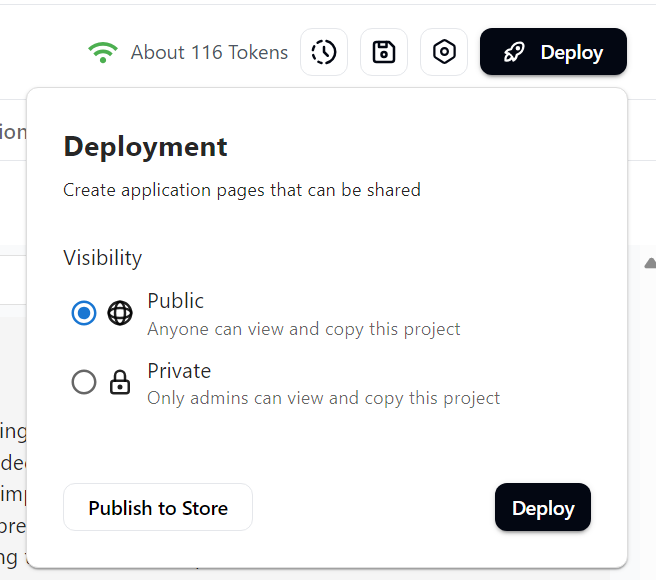
In my example, I selected public and now I can preview my agent by selecting preview in tab.
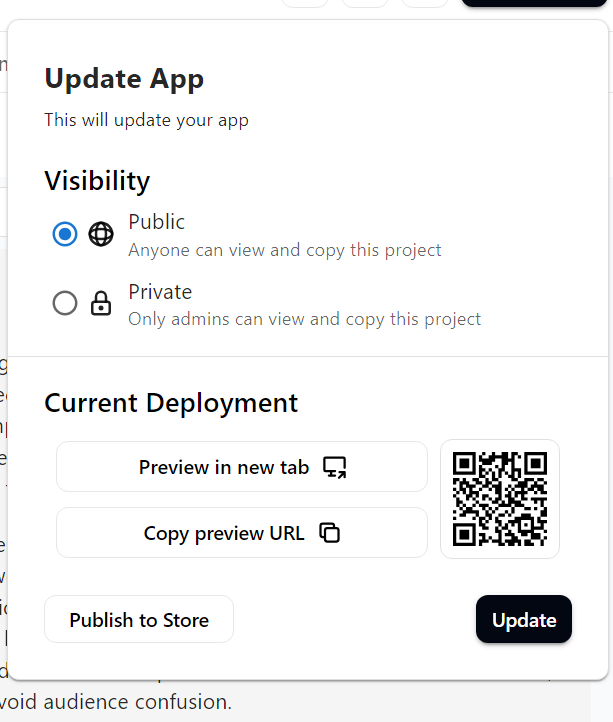
You can choose to share your agent, make more updates or publish it to the store if its ready for prime time.
Key takeaways#
- Modular Agent Design:
- Single Responsibility Principle: Each agent should have a single, well-defined purpose. This makes the system easier to understand, debug, and maintain. (For example, Transcript cleaning separate from summarization).
- Clear Roles: Explicitly define the role of each agent (e.g., "Transcript Processor," "Summarizer and Action Item Extractor," "Meeting Interface").
- Data Flow and Agent Communication:
- Defined Input/Output Definitions: Clearly specify where each agent gets its input (
From: User Input,From: Agent X) and what type of output it produces (Process,Display). This is crucial for tracing the flow of information. - Orchestration: Use an "Entry Agent" (like "Meeting Interface") to manage the overall workflow. This agent receives the initial input, calls other agents in sequence, and displays the final results. It acts as the "conductor" of your agent orchestra.
- Variable Passing: Use variables (e.g.,
{{rawTranscript}},{{cleanedTranscript}}) to pass data between agents. Aigne.io handles this, but you need to define the variables correctly.
- Defined Input/Output Definitions: Clearly specify where each agent gets its input (
- Prompt Engineering:
- Clarity and Specificity: Prompts should be extremely clear and specific about what the agent should do. Avoid ambiguity. Provide examples when needed.
- Task Decomposition: Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps within the prompt (e.g., "1. Clean the Transcript... 2. Correct Errors... 3. Format for Clarity...").
- Contextual Information: Provide relevant context to the agent (e.g., "You are a meeting transcript processor.").
- Output Formatting: Specify the desired output format (e.g., how action items should be structured:
[Who]: [What] - [Deadline]). - Handling Edge Cases: Consider and instruct the agent on how to handle situations where information is missing (e.g., "If the person responsible is unclear, state 'Unassigned.'").
- Knowledge Base Utilization: Explicit prompts on when to reference the knowledge base.
- Entry Agent as User Interface:
- Input and Output Hub: The Entry Agent serves as the primary point of interaction for the user, handling both input and output display.
- Simplified User Experience: The end-user only interacts with one agent, even though multiple agents are working behind the scenes.
